Atrial Flutter
What is Atrial Flutter?
Atrial Flutter results from a rapid atrial reentry circuit and an AV node that physiologically cannot conduct all impulses through to the ventricles. The AV junction may allow impulses in a 1:1, 2:1, 3:1 or 4:1 ration or greater, resulting in a discrepancy between atrial and ventricular rates. The AV block may be consistent or variable.
In English PLEASE!
Much like Atrial Fibrilation the Atria is firing at a greater rate than the Ventricles will accept. In Atrial Flutter these P waves are more organized and form a "sawtooth" or "flutter" pattern. The ratio is the number of P waves vs QRS complexes. The rate is usually regular but can be irregular. A-Flutter does not usually an indication of an MI. Atrial dilation is a cause of Atrial Flutter so it is usually seen in patients with congestive heart failure.
Rules for Interpretation:
Rate- atrial rate is 250-350 and the ventricle rate will vary depending on the ratio
Rythm-usually regular but can be irregular.
Pacemaker site- in the atria but outside of the SA node.
P waves- resemble a sawtooth or picket fence.
PR interval- usually constant but can vary.
QRS complex- normal.
Texbook EKG Strip of Atrial Flutter
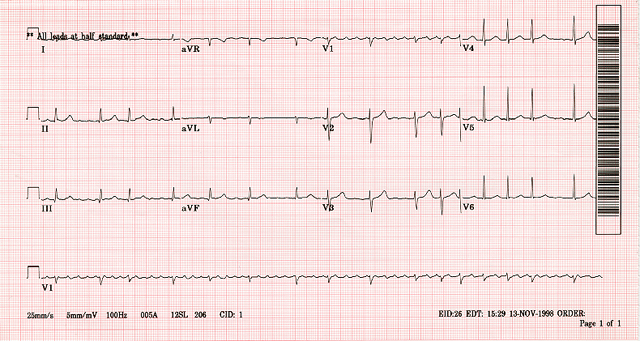
Treatment
Treatment is only indicated for rapid ventricular rates in hemodynamically unstable patient.
Treatment for Unstable Patients
Electrical Therapy- Atrial Flutter should be immediatly treated with Syncronized Cardioversion in all patients that are unstable. These patients would be complaining of pain, have a heart rate over 150, shortness of breath, altered levels of consciousness or hypotension. The patient should be treated with an IV sedative prior to cardioversion if time permits.
Pharmacological Therapy- Atria Flutter can also be treated with IV medications in paitiens who are stable and experiencing congestive heart failure. Diltiazem, Verapamil, Digoxin, Beta-Blockers, Procainamide and Quinidine may all be used. Refer to local protocols for preferred treatment.
What Will it Look Like in the Field?
[ ]
]
Dustin was on this call while doing clinicals so we can tell the story! This was a 65 year old female patient that Wisconsin Rapids Fire had brought to the ED the night before his ride along. She has a history of Atrial Flutter. Dustin arrived to Riverview CCU to find her on a Cardiezem drip at 10mg/hr. She was being transferred by Rapids Fire to Wausau to be cardioverted. In assesment the patient was able to tell the crew she had activated 911 the night before as she could feel herself going into crisis. The cardiezem was controlling her rate at 80 - 120 bpm which was comfortable to her. As you can see in the strip the ratio would go back and forth in a 3:1 and 1:1 ratio.
Group members
- Dustin Lease
- Jen Weiss
- Mark Cayce
Sources
- Brady Paramedic Care Volume 3
- Dustin Lease Clinical Testimonial
| Brady | Page #112-113 | Atrial Flutter |
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.